Revolutionising healthcare through 5G
One of the most promising applications of 5G in healthcare is the extension of specialised surgical care to individuals who face challenges in accessing treatment. Earlier this year, a landmark achievement in medical technology was realised with a live robotic telesurgery, enabled by 5G connectivity.
 |
| Rita Mokbel, head, Ericsson Vietnam |
This surgery, conducted over 10,000 kilometres – from Florida to Dubai – showcased the remarkable capabilities of 5G. The success of this telesurgery was made possible by the skills of robotic surgeons and the high-speed, low-latency connections provided by 5G tech.
This groundbreaking telesurgery demonstrates the potential for advanced technologies to deliver equitable access to healthcare, regardless of geographic barriers. In regions with limited specialist surgical expertise, telesurgery could become a vital tool, improving patient outcomes and saving lives.
Beyond telesurgery, 5G is enabling a wide range of healthcare applications, including remote patient monitoring, integrated data networks, real-time image analysis, and remote surgical assistance.
For instance, hospitals can equip patients with 5G-connected devices for continuous monitoring. By partnering with a telecom service provider and an Internet of Things healthcare provider, hospitals can secure a dedicated network slice and edge storage, processing, and AI capabilities to analyse patients’ vital signs in real time. These dedicated network slices, offering guaranteed throughput, ultra-high speeds, and near-zero latency, pave the way for live health monitoring, telemedicine, and remote surgeries – revolutionising patient care.
The benefits of 5G in healthcare are already evident. Hospitals are witnessing improvements in patient care, including enhanced pre-operative planning, faster image retrieval, and scalable hardware solutions linked to cloud systems. The use of 5G is also improving training and education for healthcare professionals and enhancing the overall patient experience.
A notable example of 5G’s potential in healthcare is the National University Health System (NUHS) in Singapore, which has developed AI software compatible with Microsoft’s HoloLens 2 AR headset. This technology assists in detecting patients’ veins, a task that can be challenging when veins are difficult to locate.
The process involves a healthcare worker placing a sticker on the patient’s arm, allowing the software to identify it and guide the AR headset to locate the veins. This method, which uses infrared light absorption by blood vessels, also frees up the healthcare worker’s hands, making procedures like drawing blood more efficient.
The NUHS has also deployed an indoor 5G network in several operating theatres and wards, where it is testing the use of HoloLens 2 for pre-operative planning. This 5G-enabled “holo medicine” allows surgeons to visualise patients’ organs in high-resolution 3D without any lag, significantly enhancing the planning and execution of surgical procedures.
Surgeons can superimpose a 3D hologram of a patient’s brain onto their field of view during surgery, enabling more precise and efficient operations. The 5G connectivity ensures that these holographic streams are smooth and lag-free, outperforming 4G or Wi-Fi.
As healthcare organisations face increasing data demands from new devices and applications, they are turning to edge architecture to bring computing power closer to the hospital while centralising data. Currently, data in hospitals often exists in silos, leading to potential misdiagnoses when diagnostic results, like MRI scans or echocardiograms, are difficult to share.
To transform healthcare, robust connectivity is essential. The foundation for this digital infrastructure lies in high-performance 5G connectivity and cloud-based solutions that enable seamless data sharing among medical experts.
Looking forward, the future of healthcare will depend on the ability to blend technological innovation with medical expertise. As new devices and place ever-increasing data demands on existing infrastructures, healthcare applications organisations are increasingly looking to edge architecture to bring computing power closer to the hospital while centralising data.
In hospitals across the world, data often exists in silos, which can lead to patients going undiagnosed when diagnostic results, like MRI scans or echocardiograms, are difficult to share. To fully transform healthcare, high-performance connectivity, and cloud software that enables easy data sharing between experts, are the essential building blocks for this new digital infrastructure.
The coming months and years will be crucial in ensuring that advancements in healthcare technology are effective, ethically sound, and technically viable. The fusion of 5G with healthcare presents an opportunity to overcome traditional barriers and drive a new era of medical innovation that could enhance patient care, improve outcomes, and make healthcare more accessible and efficient than ever before.
 | Accelerating Vietnam’s journey towards 5G 5G remains on track to become the fastest-adopted mobile generation: 5G mobile subscriptions are forecast to have topped 1.6 billion at the end of 2023, and 5.3 billion by 2030. However, we are still early in the 5G cycle and only 28 per cent of 4G sites globally have been upgraded to 5G mid-band. Likewise, only 1.6b 5G subscribers, out of a total of 8.5b mobile subscriptions, enjoy the benefits of 5G. |
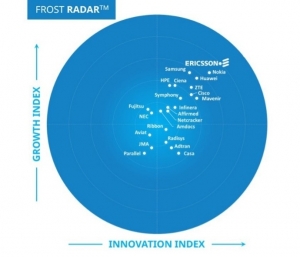 | Ericsson tops 5G network infrastructure market ranking Ericsson has been ranked top of the Frost Radar™ 5G Network Infrastructure Market 2024 analysis for the fourth consecutive year, highlighting the impact of the company’s strategy to meet the evolving needs of communications service providers (CSPs). |
 | 5G opportunities opening for enterprises in Vietnam Ericsson is working with mobile service providers to ensure Vietnam is at the forefront of 5G developments. Rita Mokbel, head of Ericsson Vietnam, discussed with VIR’s Bich Thuy how the group’s strengthened portfolio and global experiences can accelerate the 5G journey of enterprises in Vietnam. |
 | 5G building blocks falling into place While making moves in 5G infrastructure development, major network operators in Vietnam are facing financial challenges and investment return. |
What the stars mean:
★ Poor ★ ★ Promising ★★★ Good ★★★★ Very good ★★★★★ Exceptional
Themes: Digital Transformation
- PM sets five key tasks to accelerate sci-tech development
- Ho Chi Minh City launches plan for innovation and digital transformation
- Dassault Systèmes and Nvidia to build platform powering virtual twins
- Sci-tech sector sees January revenue growth of 23 per cent
- Advanced semiconductor testing and packaging plant to become operational in 2027
Related Contents
Latest News
More News
- Ho Chi Minh City launches plan for innovation and digital transformation (February 25, 2026 | 09:00)
- Vietnam sets ambitious dairy growth targets (February 24, 2026 | 18:00)
- Masan Consumer names new deputy CEO to drive foods and beverages growth (February 23, 2026 | 20:52)
- Myriad risks ahead, but ones Vietnam can confront (February 20, 2026 | 15:02)
- Vietnam making the leap into AI and semiconductors (February 20, 2026 | 09:37)
- Funding must be activated for semiconductor success (February 20, 2026 | 09:20)
- Resilience as new benchmark for smarter infrastructure (February 19, 2026 | 20:35)
- A golden time to shine within ASEAN (February 19, 2026 | 20:22)
- Vietnam’s pivotal year for advancing sustainability (February 19, 2026 | 08:44)
- Strengthening the core role of industry and trade (February 19, 2026 | 08:35)

 Tag:
Tag:




















 Mobile Version
Mobile Version