Digital transformation to radically transform manufacturing in the future
 |
| The history of manufacturing from Generation 0 to 3 |
According to the research “The Future Factory: Mapping the Skills That Will Power Manufacturing”, the workforce analysis describes the impacts of the digital transformation on the manufacturing sector and highlights the roles of innovation culture and other leadership skills to the business transformation’s success.
Digital transformation with breakthroughs in advanced technology is taking place in every sector globally, including manufacturing. As the vanguard of digital transformation, the industry’s transition to full digitisation is already well underway and accelerating daily. In tandem with that process, new roles appear with advanced digital skills demanded while others become obsolete.
Since the early days of its history, manufacturing has undergone and evolved through four technical generations – Generations Zero to Three. Each generation is aligned to different eras of manufacturing tools, technologies, and work. Today, we are on the cusp of the third generation, characterised by the transformational power of radical improvements in connected systems and machine learning, and we expect to be fully immersed in Gen Three by 2020.
The groundbreaking workforce analysis identifies 165 new and evolving roles across seven areas of technical expertise in manufacturing, including: digital manufacturing, digital thread, digital enterprise, digital product, digital design, supply network, and omni. The impact of transformation differs for each domain with the greatest shift occurring in the Digital Manufacturing – 28 per cent of the 165 new or evolved roles are in this domain. Within the seven domains above, specific roles can be mapped by the impact they make on the organisation and the way they connect to each other.
“In order to develop the talent they need to remain competitive, manufacturing companies need new approaches for training, that is, to up-skill and re-skill people at speed and at scale. It is now or never,” said Le Thi Kim, head of Staffing and Outsourcing Services, North, ManpowerGroup Vietnam. From the researchers’ findings, the most effective skills development and retention are achieved through certification programmes of six months or less or on-the-job training.
The manufacturing’s technological transformation also proposes a need for leadership roles to change. Managers and leaders should follow the 80/20 rules to stay relevant and competitive. While foundational leadership skills keep playing an integral part, effective leaders must also nurture the additional 20 per cent – an innovation culture and risk management, learnability, adaptability, and optimising opportunities.
The key to catching the shift of digital transformation and skills revolution in manufacturing is a connected workforce strategy at the soonest. Besides investing in internal talent via a development programme, helping people transit to new roles when necessary, employers should cultivate and connect communities of talent beyond the organisation, especially going to the labour market or workforce solutions providers to attract the talent that cannot be built in-house.
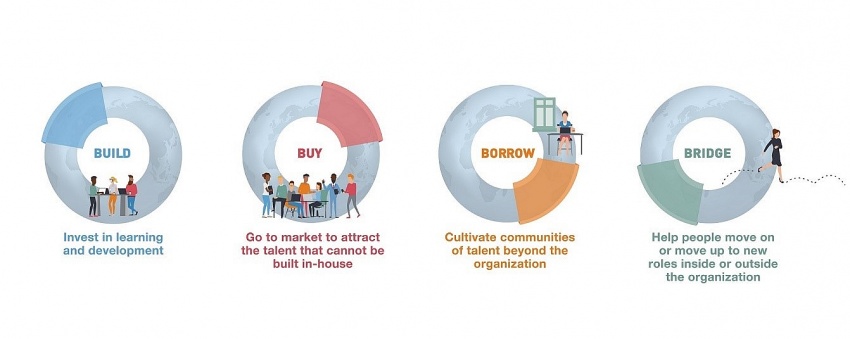 |
| 4B strategy |
Particularly, based on ManpowerGroup’s workforce analysis of 165 new and evolving roles across seven “domains” of technical expertise, manufacturing organisations can identify future talent needs in the short, medium, and long term.
| About the research The groundbreaking workforce analysis was jointly developed by ManpowerGroup and MxD (formerly the Digital Manufacturing and Design Innovation Institute) with the purpose to find practical solutions to the skills shortage and ensure up to two million new manufacturing jobs in the US do not go unfilled. ManpowerGroup and MxD convened more than 30 academic, government, and industry partners including Siemens, Microsoft, Caterpillar, and General Electric to create an industry-recognised taxonomy that defines digital manufacturing roles of the future, serving as a practical toolkit for manufacturing organisations. |
 Future of manufacturing: Up- and re-skilling during a tech revolution Future of manufacturing: Up- and re-skilling during a tech revolution |
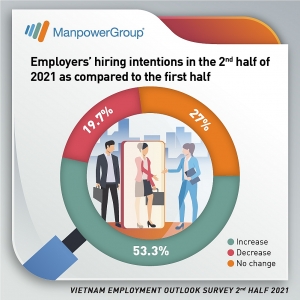 Vietnam: Hiring intentions stay positive in second half Vietnam: Hiring intentions stay positive in second half |
 Talent shortage in second half of 2021 and the way out Talent shortage in second half of 2021 and the way out |
What the stars mean:
★ Poor ★ ★ Promising ★★★ Good ★★★★ Very good ★★★★★ Exceptional
Related Contents
Latest News
More News
- Green jobs needed as businesses embrace sustainability (April 06, 2023 | 11:24)
- HR leaders urged to handle work management in global uncertainty (October 20, 2022 | 17:07)
- Facing the biggest HR challenges in 2022 (October 10, 2022 | 12:14)
- Solving talent shortages amid fierce human capital landscape (August 26, 2022 | 16:18)
- Employers expect hiring to increase in H2 (August 13, 2022 | 21:30)
- Stakeholders seek sustainable strategies to retain workers (June 21, 2022 | 17:54)
- Accelerating trends and renewed urgency for labour (May 05, 2022 | 14:25)
- Latest HR trends in logistics revealed (April 28, 2022 | 14:38)
- Sustainable employment under digital transformation and the pandemic (October 29, 2021 | 15:04)
- Employment security and the future of skills for Vietnamese workers in digital transformation (October 26, 2021 | 17:20)

 Tag:
Tag:




















 Mobile Version
Mobile Version