Innovations in Schneider Electric’s links
 |
One such group, Schneider Electric, was recently ranked 11th in The Gartner Supply Chain Top 25 for 2019, and also won Gartner’s 2019 Industrial Manufacturing Supply Chainnovator award.
The award is a research and recognition programme to celebrate innovation in the supply chain. Companies recognised as a “chainnovator” have shown an ability to innovate successfully and develop high-impact approaches to transform the industrial supply chain.
The award has become internationally recognised since its establishment in 2017. This year there have been a significant number of submissions, which demonstrates the increasing importance of supply chain innovation, the rapid change in technology and the continuous need to upskill workforce competencies.
As industrial manufacturers are working to speed up innovation cycles, become more customer-centric, and continue to deliver operational excellence, digital transformation becomes the key to unlocking the next set of improvements. Sensors and smart devices in manufacturing and distribution, optimising network capacity, and automating repetitive tasks are some typical examples of innovation.
Schneider Electric sees the essential challenge of the future is to prepare the workforce for the coming changes of a developing economy. In order to overcome this challenge, the company has implemented a strategy that identifies the competencies most-needed for this transformation, and helps employees develop these skills. This initiative aims to map, anticipate, and grow Schneider Electric’s digital acumen and competencies by assessing the company’s current and future use of technology.
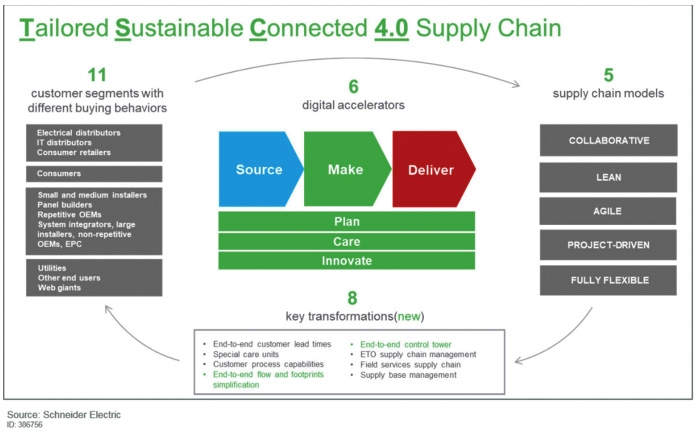
The project is critical to Schneider Electric’s Tailored Sustainable Connected 4.0 supply chain. It aims to develop six digital enablers — product innovation, planning, procure-to-pay, manufacturing, distribution, and customer care — and result in identifying 16 competencies across technical, analytical, and soft skills.
The supply chain has adopted its commercial EcoStruxure platform, which includes augmented reality for operators, robots, automated guided vehicles, and 3D printing for non-production parts. The implementation of the platform has led to sweeping changes in the production process, which requires different competencies for success. The EcoStruxure platform is in alignment with the company’s long-term strategy in Southeast Asia.
As Yoon Young Kim, country president of Schneider Electric Vietnam, Myanmar, and Cambodia said, “EcoStruxure has been shaping up as the key solution to helping Vietnam manage energy efficiently and catch up with the trend of digital transformation. We will continue to research and introduce international standard products at reasonable prices in Vietnam, especially with an emphasis on EcoStruxure solutions. We are ready to accompany Vietnamese enterprises in the Fourth Industrial Revolution.”
Schneider Electric, the leading company in digital transformation of energy management and automation, is continuing to upgrade factories around the world to smart factories, and upskill the workers within those factories. As of 2018, Schneider Electric’s global supply chain operation, comprised of 200 manufacturing plants in 46 countries and 98 distribution centres, saw its 86,000-strong workforce manage over 260,000 references and proceed over 150,000 order lines daily.
To date, more than 50 of Schneider Electric’s manufacturing locations have been converted to smart factories, with plans for a further 100 sites to be converted by the end of 2020. The company owns a significantly large supply chain and is applying digital transformation to help this system operate smoothly and efficiently.
As for success thus far, reports of quality issues have fallen thanks to a greater ability to understand predictive maintenance and anticipate process deviation. Other companies may be able to learn from businesses like Schneider Electric in its mapping of new competencies and its digital age employee training.
What the stars mean:
★ Poor ★ ★ Promising ★★★ Good ★★★★ Very good ★★★★★ Exceptional
Related Contents
Latest News
More News
- Efficient technology solutions key factors in energy transition (September 25, 2024 | 09:00)
- Sao Do Group gears towards energy savings (December 07, 2023 | 12:01)
- Vice President Vo Thi Anh Xuan visits Copenhagen Infrastructure Partners headquarters (November 23, 2023 | 10:37)
- A wind turbine tower collapses in China (November 20, 2023 | 19:36)
- Vietnam has massive potential for offshore wind energy (March 17, 2023 | 16:29)
- Rooftop solar event entices EPC contractors and investment funds (March 09, 2023 | 07:50)
- GreenYellow acquires 49.5MWp solar farm of French IPP Qair in Vietnam (November 25, 2022 | 08:00)
- Eaton contributes to Vietnam’s low-carbon economy (November 20, 2022 | 19:00)
- Proposals to promote Vietnam's energy transition (November 12, 2022 | 22:02)
- How intelligent lights make cities smarter, safer and greener (November 04, 2022 | 09:00)

 Tag:
Tag:




















 Mobile Version
Mobile Version