Vietnam unlocking digital potential
A series of sizeable digital investments in ASEAN recently attracted our attention.
The region has become more tech-savvy in the past two decades, with Vietnam clearly standing out. Based on the e-Conomy SEA report, Vietnam was the fastest-growing digital economy in ASEAN last year, with the potential to become the second-largest one by 2030. Thanks to its large consumer base and rising number of internet users, it is not difficult to understand the potential in its digital economy.
However, many challenges remain. For one, how to increase Vietnam’s digital literacy remains a priority, as Vietnam has been lagging regional peers. Encouragingly, the National Digital Transformation Programme is an example where the public sector seeks to play an active role to facilitate the digital transformation of the economy. Meanwhile, how to secure the additional energy necessary to fuel the momentum is another challenge, as shown in the case of data centres.
Heading towards the end of the first half of the year, Vietnam remains on track for an external-led recovery. That said, it is still not broad-based, with the electronics sector taking the lead. Meanwhile, the domestic recovery continues to lag, with muted monthly retail sales performance. Outside of growth, inflation continued to hover close to the 4.5 per cent ceiling in May. The performance was a mixed picture in the food and energy segments, warranting a close watch in the near term.
A flurry of digital-related investments has been taking place in Southeast Asia. Microsoft recently announced a number of investments in Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand. In Vietnam, Alibaba plans to construct a data centre to accommodate rising digital demand. Clearly, with much focus on tapping into the rising digital economy in Vietnam, it is useful to have a closer look at some of the fundamentals at play.
With a population of over 100 million and a working age share of close to 70 per cent, we see the strong potential for Vietnam’s digital consumption.
According to the e-Conomy SEA 2023 report, Vietnam was the fastest-growing digital economy in ASEAN with impressive growth of 20 per cent. Measured by gross merchandise value, the country has the potential to become the second-largest digital market in the region by 2030, just after Indonesia (Chart 1). We expect the expansion to be led by a rapidly developing e-commerce ecosystem, supported by a rising consumer base.
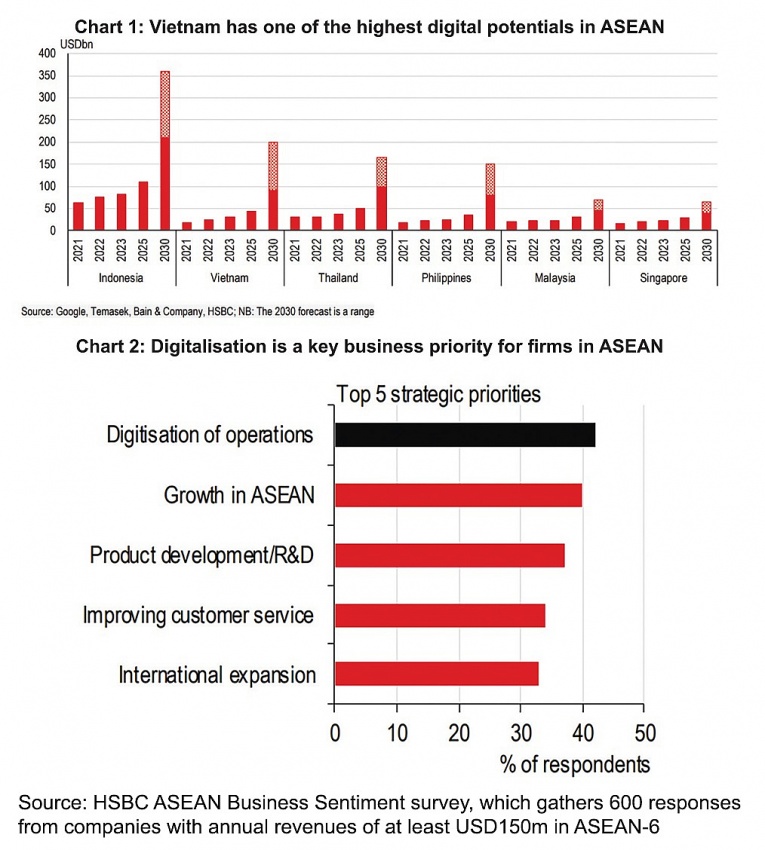 |
But it is not just the demographic tailwinds - Vietnam’s rapid rise in internet users also helps expand its digital market. Almost 80 per cent of Vietnam’s population now use the internet, thanks to smartphone ownership more than doubling from a decade ago.
However, despite the considerable growth in internet users, the application of digital technologies in certain areas has lagged. According to the World Bank’s 2021/22 data, Vietnam lagged Singapore, Thailand, and Malaysia in terms of using non-cash payment methods, although efforts to transition to digital payments have accelerated since then.
Meanwhile, digital transformation has more room to run in areas beyond consumers. Trade, for example, is still relatively paper-based. This can risk imposing additional costs and delays, serving as a bottleneck on trade flows. Although increasing use of the National Single Window, an online platform to process trade documents between firms and the government, has led to material improvements in customs clearance efficiency, some hurdles remain.
For example, the use of digital signatures remains limited, meaning some procedures still need to be handled by paper. Alternative measures of digital integration within trade suggest further room to transition to paperless paperwork.
That said, part of the challenge stems from lagging digital literacy of the population, which has hindered the adoption of digital tools and constrained their effective use. In terms of digital skills and talent, Vietnam lagged its peers, limiting the upside from digitalisation.
Encouragingly, the government is well aware of these challenges, and has been playing an active role to facilitate the digital transformation of the economy. In accordance with the National Digital Transformation Programme through 2025 with a vision to 2030, Vietnam aims to build the three pillars of digital government, digital economy, and digital society. The government has correspondingly laid out a number of ambitious targets in recent years, including handling all administrative procedure applications online by 2030.
The national strategy opens up opportunities in a wide range of sectors. In particular, digital literacy is relatively low among the rural population and in the agricultural sector. At the end of 2021, there were more than 27,000 agricultural cooperatives, but only about 2,000 applied ‘high-tech’ and digital technology in production. Furthermore, these groups typically still depend more on traditional financing methods.
While state-led initiatives to drive rural digitalisation have spurred progress in building a digital economy, it is important to note that private businesses can also play a role in accelerating the transition. For example, Grab conducted training workshops for over 800 cooperatives to help farmers learn about digitalisation and related business opportunities.
Another important consideration is how to secure the additional energy needed to fuel the momentum. A contributing factor is a decree, originally introduced in 2022, which requires firms to store data locally. Future proliferation in the volume of local data suggests more data centres being built, as was likely a partial factor in Alibaba’s decision to construct a data centre locally.
This highlights the linkage between growth in the digital economy and the availability of energy, of which the latter has already seen some challenges. Power outages last May and June were estimated by the World Bank to have cost 0.3 per cent of GDP, particularly affecting manufacturing firms. As electricity demand looks set to expand further, expanding and improving Vietnam’s energy supply and infrastructure will become more important.
All in all, digitalisation brings both opportunities and challenges to Vietnam. To leverage its favourable demographics and achieve its digital ambitions, investments need to be channelled into not just new areas such as AI, but also foundational areas such as digital education and traditional infrastructure.
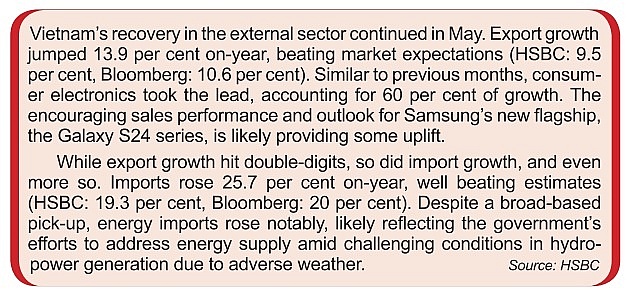 |
In fact, this drive is not just happening in Vietnam, but in ASEAN as a whole. According to a recent HSBC survey, more than 40 per cent of surveyed businesses operating in ASEAN rank digitalisation as a top priority (Chart 2). Therefore, active dialogue and partnerships between the public and the private sector can help accelerate these developments to prepare for a more digitally fit population.
 | Digital transformation and applying AI in journalism In 2023, the government established a national strategy for the digital transformation of media, with the ambitious goal that by 2030, most media agencies in Vietnam must switch to digital. According to this strategy, all Vietnamese media agencies must reconstruct their newsrooms toward digital convergence. |
 | Siemens presents sustainable industrial innovations at VIMF 2024 Siemens showcased groundbreaking industrial solutions at the Vietnam Industrial & Manufacturing Fair 2024 (VIMF 2024), held from June 19 to 21 in Binh Duong province. |
 | Cisco launches digital acceleration programme in Vietnam On June 20, Cisco, a global tech leader , announced the launch of its Country Digital Acceleration (CDA) programme in Vietnam. |
(*) Yun Liu, ASEAN economist HSBC Global Research
What the stars mean:
★ Poor ★ ★ Promising ★★★ Good ★★★★ Very good ★★★★★ Exceptional
Related Contents
Latest News
More News
- Citi economists project robust Vietnam economic growth in 2026 (February 14, 2026 | 18:00)
- Sustaining high growth must be balanced in stable manner (February 14, 2026 | 09:00)
- From 5G to 6G: how AI is shaping Vietnam’s path to digital leadership (February 13, 2026 | 10:59)
- Cooperation must align with Vietnam’s long-term ambitions (February 13, 2026 | 09:00)
- Need-to-know aspects ahead of AI law (February 13, 2026 | 08:00)
- Legalities to early operations for Vietnam’s IFC (February 11, 2026 | 12:17)
- Foreign-language trademarks gain traction in Vietnam (February 06, 2026 | 09:26)
- Offshore structuring and the Singapore holding route (February 02, 2026 | 10:39)
- Vietnam enters new development era: Russian scholar (January 25, 2026 | 10:08)
- 14th National Party Congress marks new era, expands Vietnam’s global role: Australian scholar (January 25, 2026 | 09:54)

 Tag:
Tag:


















 Mobile Version
Mobile Version